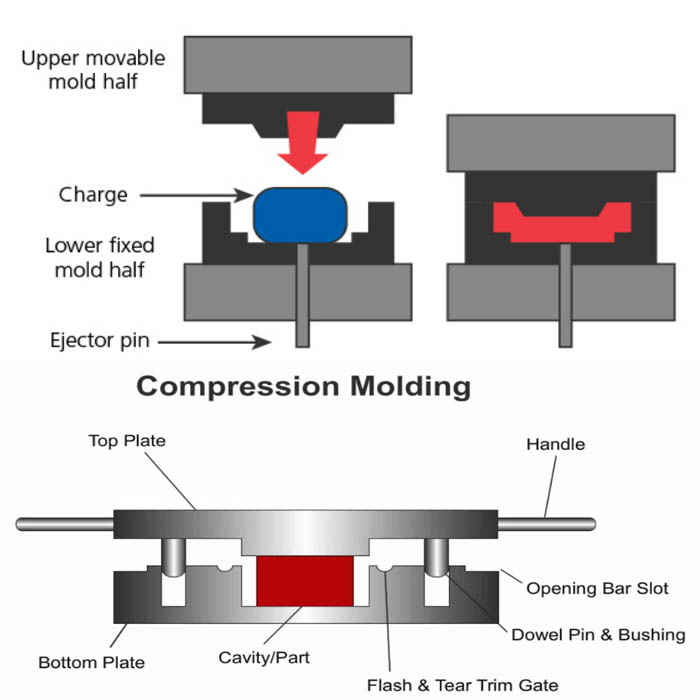
Compression molding (also known as compression molding or compression molding) is an operation that first puts powdered, granular or fibrous plastic into a mold cavity at the molding temperature, and then closes the mold to press to shape and solidify it. Compression molding can also be used for thermosetting plastics, thermoplastics and rubber materials.
Scope of application
Mainly used as structural parts, connectors, protective parts and electrical insulation parts. It is widely used in industry, agriculture, transportation, electrical, chemical, construction, machinery and other fields. Because of the reliable quality of molded products, they have also been used in weapons, aircraft, missiles, and satellites.

Advantage
(1) The loss of raw materials is small and will not cause too much loss (usually 2% to 5% of the product quality).
(2) The internal stress of the product is very low, and the warpage deformation is also very small, and the mechanical properties are relatively stable.
(3) The wear of the mold cavity is small, and the maintenance cost of the mold is low.
(4) The cost of molding equipment is low, and its mold structure is simpler, and its manufacturing cost is usually lower than that of injection molds or transfer molding molds.
(5) Larger flat-shaped products can be formed, and the size of the products that can be formed by molding is only determined by the clamping force of the existing molding press and the size of the template.
(6) The shrinkage of the product is small and the repeatability is good.
(7) A mold with a large number of cavities can be placed on a given template, and the productivity is high.
(9) It can be adapted to automatic feeding and automatic taking out of products.
(10) High production efficiency, easy to realize specialized and automated production.
(11) The product has high dimensional accuracy and good repeatability.
(12) The surface is smooth and clean without secondary modification.
(13) Products with complex structures can be formed at one time.
(14) Mass production, relatively low price.
Process flow
(1) Feeding: Add a specified amount of material to the mold as needed, and the amount of feed directly affects the density and size of the product. If the amount of feed is large, the product will have thick burrs, poor dimensional accuracy, difficult to demold, and may damage the mold; if the amount of feed is small, the product will not be tight, with poor gloss, and even cause shortage of materials and waste products.
(2) Mold closing: even if the male and female molds are closed after feeding. When closing the mold, use fast speed first, and change to slow speed when the male and female molds are in quick contact. The quick first and slow operation method is beneficial to shorten the non-production time, prevent the mold from scratching, and avoid the raw material in the mold cavity from being carried out by the air due to the rapid clamping of the mold, and even the displacement of the insert and the destruction of the molding rod. After the mold is closed, the pressure can be increased to heat and pressurize the raw materials.
(3) Exhaust: Moisture and low-molecular substances are often released when molding thermosetting plastics. In order to remove these low-molecular substances, volatiles and air in the mold, the plastic reaction in the cavity of the plastic mold can be used for a suitable time. It takes a very short time to release the pressure and release the air. The air exhaust operation can shorten the curing time and improve the physical and mechanical properties of the product, and avoid stratification and bubbles inside the product; but the exhaust is too early, sooner or later, and too early. To the exhaust purpose; too late, the gas cannot be exhausted due to the solidified surface of the material.
(4) Curing: The curing of thermosetting plastics is to keep them at the molding temperature for a period of time, so that the polycondensation reaction of the resin reaches the required degree of crosslinking, and the product has the required physical and mechanical properties. Plastics with a low curing rate can also be cured temporarily when the product can be completely demolded, and then post-processing is used to complete the entire curing process; in order to improve the utilization rate of the equipment. The molding curing time is usually the holding pressure and holding time, generally ranging from 30 seconds to several minutes, and most of them do not exceed 30 minutes. Too long or too short curing time will affect the performance of the product.
(5) Demoulding: Demoulding is usually done by ejector rods. Products with molding rods or some inserts should be removed first with special tools, and then demolded.
(6) Mold blowing: After demolding, the mold cavity and mold surface are usually blown with compressed air. If the fixation on the mold is tight, it can also be cleaned with a copper knife or a copper brush, or even a polishing agent brush, etc. .
(7) Post-treatment: In order to further improve the quality of products, thermosetting plastic products are often post-treated at a higher temperature after demolding. Post-treatment can make the plastic curing more complete; at the same time, reduce or eliminate the internal stress of the product, reduce the moisture and volatile matter in the product, etc., which is beneficial to improve the electrical performance and strength of the product .
MB/Wechat/Whatsapp:+0086-13456489912
sophiemould@foxmail.com


Post time: Jul-01-2021
